improving thermal conductivity with Borone Nitride
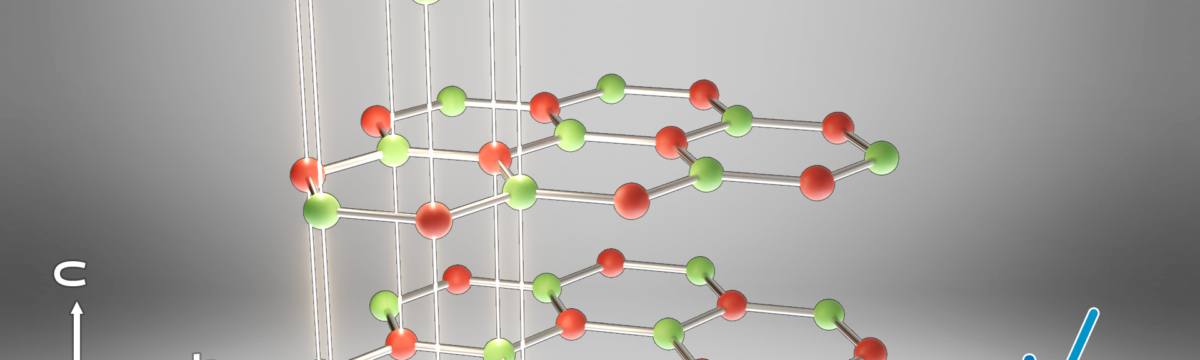
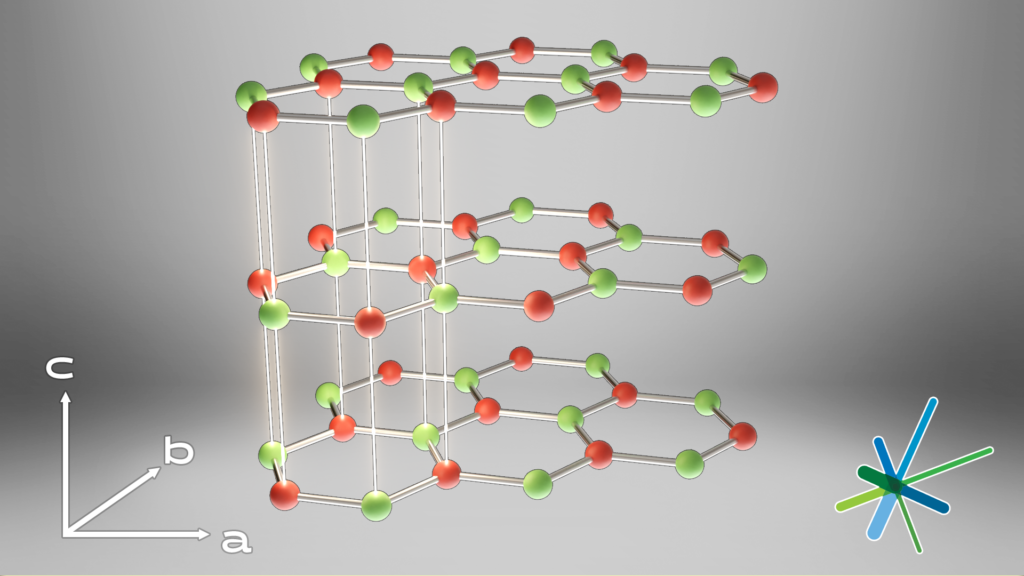
Boron Nitride (BN) is one of the most attractive fillers for improving thermal conductivity while maintaining the electrical insulation of polymeric thermal management materials used in electronic devices. Thermal management materials loaded with Boron Nitride (BN) match the challenge of offering thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, low coefficient of thermal expansion, and low density. However, due to the anisotropic thermal transport in the laminar BN crystal structure, thermal management materials filled with platelet shape BN as thermal filler often have anisotropic thermal performance – one magnitude lower thermal conductivity in through-plane direction than in-plane direction. At the same loading in polymer thermal management materials, platelet BN particles lack the efficiency to form heat-conductive channels in a direction not aligned with the platelet orientation, typically caused by exposure to high shear in the compounding process.
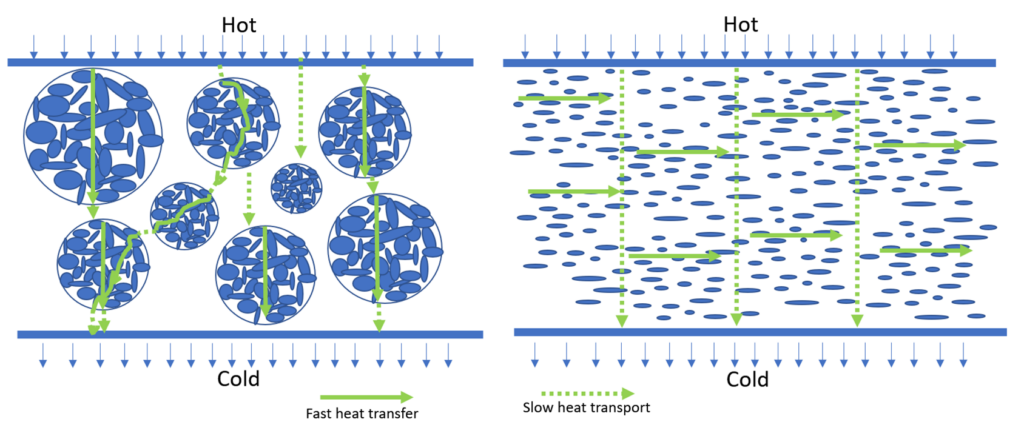
As illustrated in the figure below, randomly oriented BN platelets composing the agglomerates can form more efficient heat conductive channels in all directions to enable high isotropic thermal performance in thermal management materials.
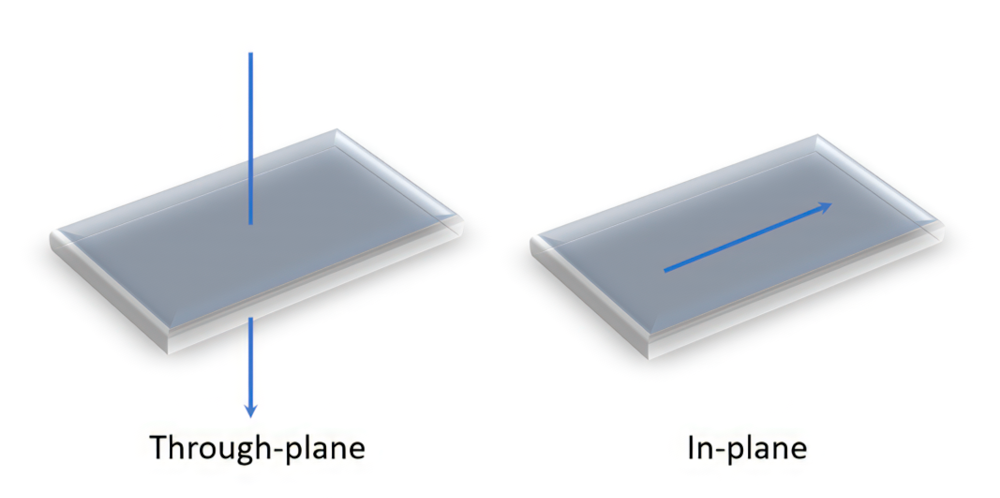
In MT’s high performance agglomerate BN powder portfolio, PTX series grades, benefiting from its spherical agglomerate shape, can enable users to achieve the best isotropic thermal performance in filled composites. As shown in the example below, in the thermal performance comparison between the spherical agglomerate BN powder grade PTX60 and platelet BN powder grade PT110 similar particle size, PTX60 enables almost identical excellent thermal conductivity in both in-plane and through-plane directions, while PT110 can be oriented during compounding process and exhibit very anisotropic thermal performance. Therefore, spherical agglomerate BN such as PTX60 has been the top choice for thermal management materials design requiring the best isotropic thermal performance.