Electric Vehicles
Home | Applications | Electric Vehicles
The Essential Role of Thermal Management in Elevating EV Performance
Effective thermal management in battery-powered electric vehicles is essential for performance, reliability, and durability. These vehicles operate best at optimal temperatures—not too hot or cold—which are crucial for the battery pack, power electronic systems, and motor. Maintaining these temperatures preserves battery charge and capacity and ensures power systems and motors function efficiently.
Power electronic systems are responsible for controlling electric motors. Power electronic systems operate in line with the electric vehicle control system and drive the electric motor according to the control instructions. The power electronic system’s DC-DC converters, inverters, and control circuits are vulnerable to thermal effects. While working, the power electronic circuits generate heat loss, and proper thermal management is essential to release the heat from the circuit and associated systems. If the thermal management is insufficient, it can result in control glitches, and component failures. Usually, the power electronic system is connected to the electric vehicle’s cooling system to maintain optimal temperatures.
The industry is striving for higher power output, increased voltage, faster data transmission, lighter weight, and more compact sizes. To address these thermal management challenges, there is a need for thermally conductive yet electrically insulating thermal interface materials (TIMs) that feature high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant. While TIMs made from dielectric polymers are naturally insulative, incorporating ceramic fillers enhances their thermal conductivity while still maintaining electrical resistance. The exceptional thermal and dielectric properties of these ceramic thermal fillers are crucial for the effectiveness of thermal management materials.
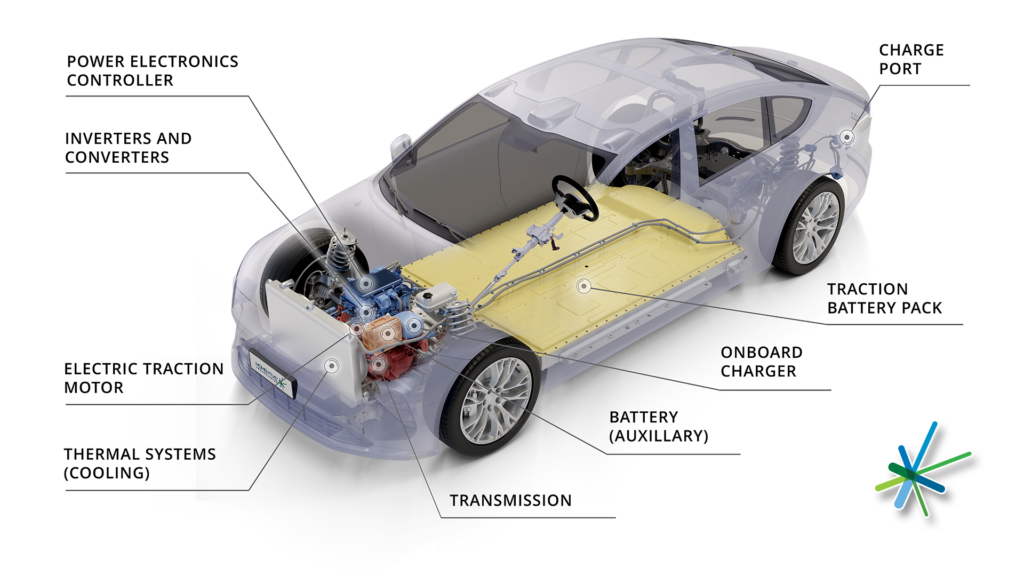
Power Electronics Systems
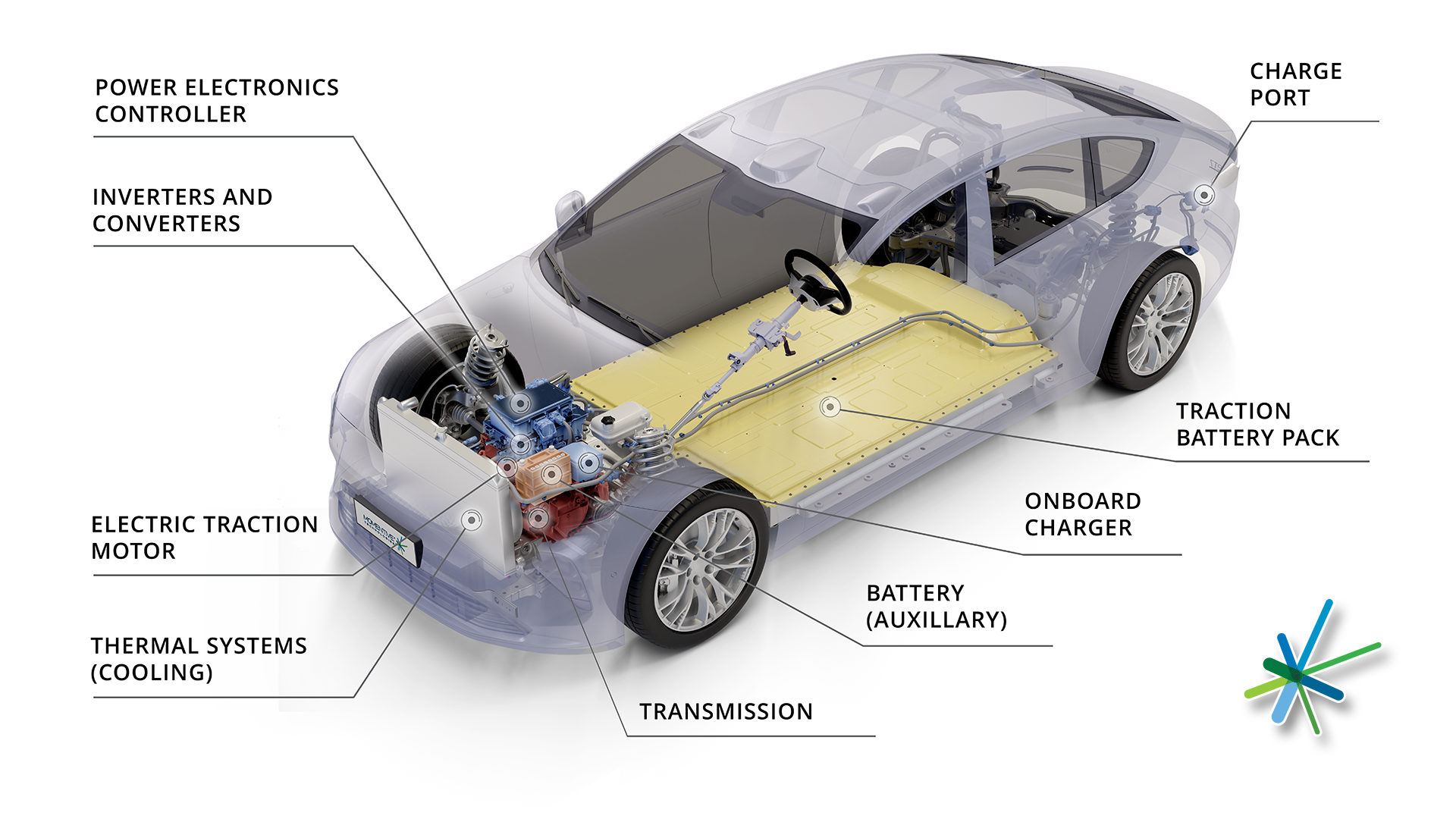
Click image to enlarge
Read articles about our advanced materials and technologies and their enabling Electric Vehicles:
Boron Nitride: Rising to the Challenge
Boron nitride (BN) is a versatile compound with unique properties that are gaining importance in electric vehicle applications. This synthetic ceramic consists of boron and nitrogen atoms in a hexagonal lattice, resembling graphite, but it outperforms many materials, including graphite, in critical applications. Boron nitride is widely used in electric vehicles for several essential components. It is a thermally conductive filler in polymer materials like encapsulation resin and TIMs. BN is also used as a coating in the superplastic forming of aluminum autobody panels to reduce weight and as a non-stick release agent in high-temperature manufacturing.
Additionally, BN is utilized as a high-temperature insulator cap for wiring and in producing EV batteries due to its non-reactivity with standard materials. With its outstanding thermal conductivity, inertness, high dielectric strength, and lubricity, BN is being explored for numerous applications in the EV industry.
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is a synthesized ceramic material with unique crystal structure. It has good thermal conductivity, great electrical resistivity, excellent high temperature resistance and chemical inertness, and many other interesting features not easily found in regular ceramic materials.
Products Used in Electronics
Boron Nitride Powders
Our unique BN expertise allows us to tailor various powder characteristics like purity, crystallinity, surface area, particle size, etc. We are constantly adding new grades to enable new applications and maintain our position as the preeminent supplier of boron nitride powders.
Spherical Alumina
Spherical Alumina powders are used in the manufacturing process of thermal management products, which are relied on to regulate the temperature of electronic systems and devices.

